A cosmic collection of old Soviet space imagery
- Text by Joseph Marczynski
- Illustrations by The Moscow Design Museum
A blue alien gazing at a visualisation of the universe; an astronaut diving into an underwater space station; an underground society on a faraway planet.
It’s all the stuff of science fiction, certainly. But these scenes also happen to be ones plucked from the predictions and aspirations of the Soviet Union during the Space Race – at least according to images taken from a century of imagery produced there.
Released by Phaidon, in collaboration with the Moscow Design Museum, the aptly titled Soviet Space Graphics collects 250 imaginative visualisations of space travel from magazines, pamphlets and posters distributed across the former Soviet Union. According to Alexandra Sankova, founder and Director of the Moscow Design Museum, the images offer a unique window into cultural practice in the USSR at that time.

Young Technician, issue 7, 1968, illustration by R. Avotin. Picture credit: The Moscow Design Museum
“Graphic design was reflecting what was going on in the world,” she says. “Space and the future was a breath of freedom. They could imagine how the future [would] be – the intelligent, brave Soviet men who will be living in the other realities and the other worlds.”
The images themselves seem oddly prescient: much of the spacecraft images could be concept art for Star Wars, or any number of modern science fiction blockbusters. According to Sankova, artists seized the opportunity to be creative when tasked with depicting future space travel, viewing it as an escape from the rigid confines of Soviet Communism. “Space exploration was a propaganda instrument in general, because the everyday life was quite boring and grey.”
In the ’60s and ‘70s, as the Soviet Union relaxed its borders, the optimism associated with the period was evident in its imagery. “It shows the whole mood. Everyone thought, now the borders of the country have opened, we are more open to the world: we’re more open to space. This is like a very bright period in the Soviet Union. That’s why these images are so lively and so positive.”
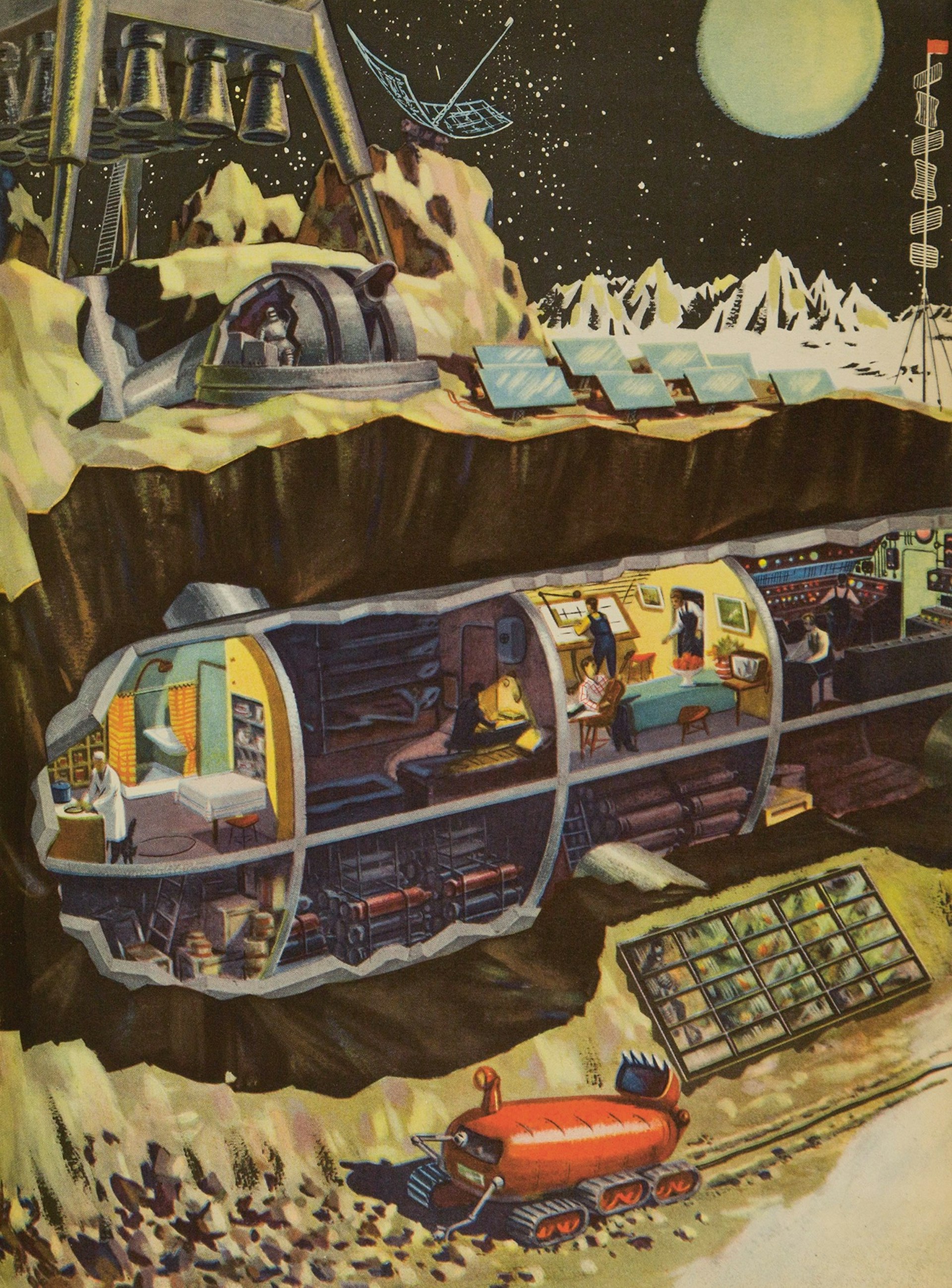

Technology for the Youth, issue 2, 1959, illustration by B. Dashkov for the article ‘What Would a Space Station on the Moon Look Like?’ Picture credit: The Moscow Design Museum
Space travel was an idea deeply ingrained in the psyche and culture of the Soviet Union from as early as the 1920s. Incredible visions of the future were ever-present in the homes of Sankova’s parent’s generation: thanks to a constant supply of material from the government, families grew up with dreams of manning space stations and settling on distant planets. Imagery of a glorious space age were everywhere, from tablecloths to children’s toys. “It was integrated into everyday living. Every city has playgrounds with the rockets on them.”
Soviet Space Graphics also provides a reflection of the fierce contest with the United States. Images like ones found in this collection were a key part of portraying the USSR as a thriving, modern society – one in direct competition with the West.
An excerpt from the publication explains how the spreading of ideology was key a key component in Soviet science fiction during the early 1920s. For instance, in Alexey Tolstoy’s Aelita – of which an excerpt in Soviet Space Graphics refers to as “the first cosmic book of science fiction’s early period” – an interplanetary explorer travels to Mars, before swiftly bringing about a Communist revolution there.

Technology for the Youth, issue 11, 1965, ‘Satellite for Everyone’, illustration by O. Yakovlev. Picture credit: The Moscow Design Museum
In the present day, this month sees the 59th anniversary of soviet cosmonaut Yuri Gagarin’s first space flight and orbit of Earth. To commemorate, Sankova’s daughter’s homework is to visualise his journey in space. Even now, she says, space travel and the pursuit of the future remains a key part of Russia’s identity. Spreading Communism to the outermost reaches of the universe may no longer be the aim, but the impact of the optimism and creativity of this period on the national psyche cannot be underestimated.
“These images were escape for many people, looking through the magazine thinking how they’re going to live in the future,” says Sankova. “I don’t think for Americans, space exploration had the same strong ideology like in the Soviet Union.”

Technology for the Youth, issue 4, 1956, illustration by A. Pobedinsky for the article ‘Brain Emits Stars on the Oscilloscope Screen’, which speculates on the existence of telepathy, and whether the human brain emits elecromagnetic waves and signals. Picture credit: The Moscow Design Museum
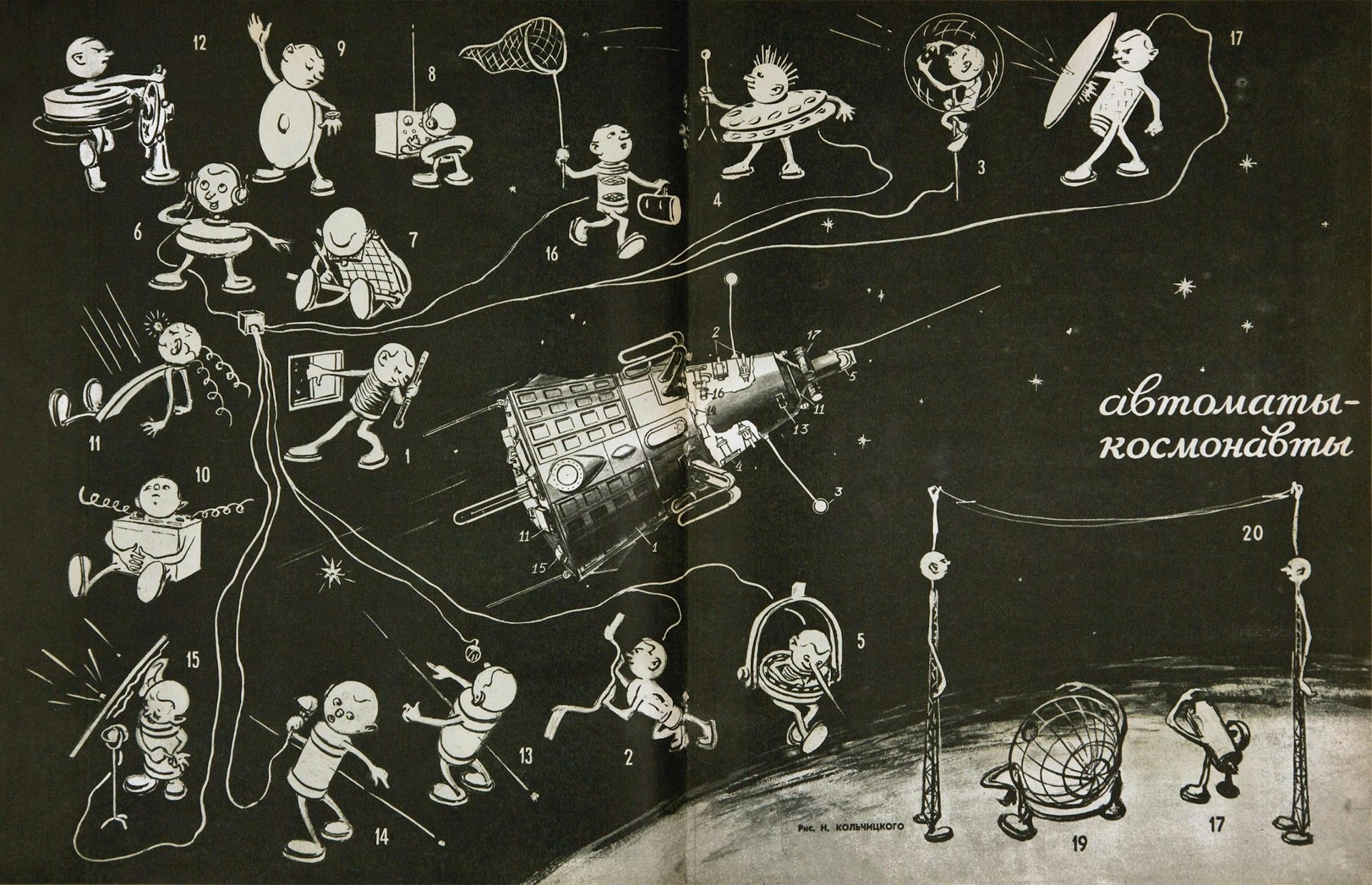
Technology for the Youth, issue 8, 1958, ‘Machines – Astronauts’, illustration by N. Kolchitsky showing the individual components of Sputnik 3 as different characters. Picture credit: The Moscow Design Museum
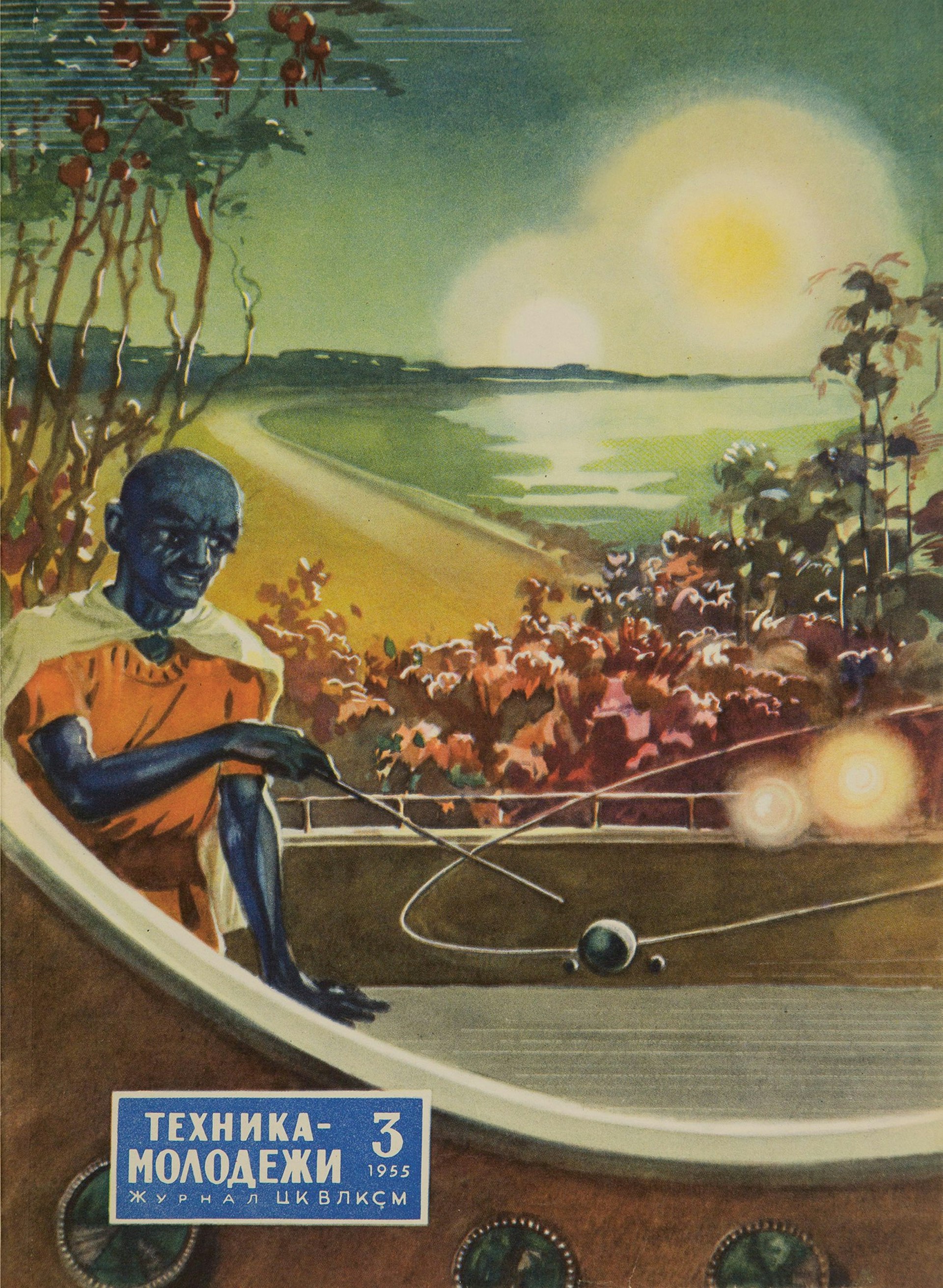

Technology for the Youth, issue 3, 1955, illustration by N. Kolchitsky.
Picture credit: The Moscow Design Museum

Young Technician, issue 10, 1964, illustration by R. Avotin for the article ‘Space Greenhouse’, which hypothesizes on the creation of an environment suitable for growing plants in space. Picture credit: The Moscow Design
Soviet Space Graphics is out now on Phaidon.
Enjoyed this article? Like Huck on Facebook or follow us on Twitter.
